Definitions
Real-valued matrix: a rectangular array of real numbers (same for interger-valued, complex-valued etc.) Matrix size: , or by matrix has rows and columns or the -entry refers to the entry in row and column
Representing Matrices
A matrix can be defined by a formula on its entry, e.g. represents a 2 by 3 matrix where the -entry is
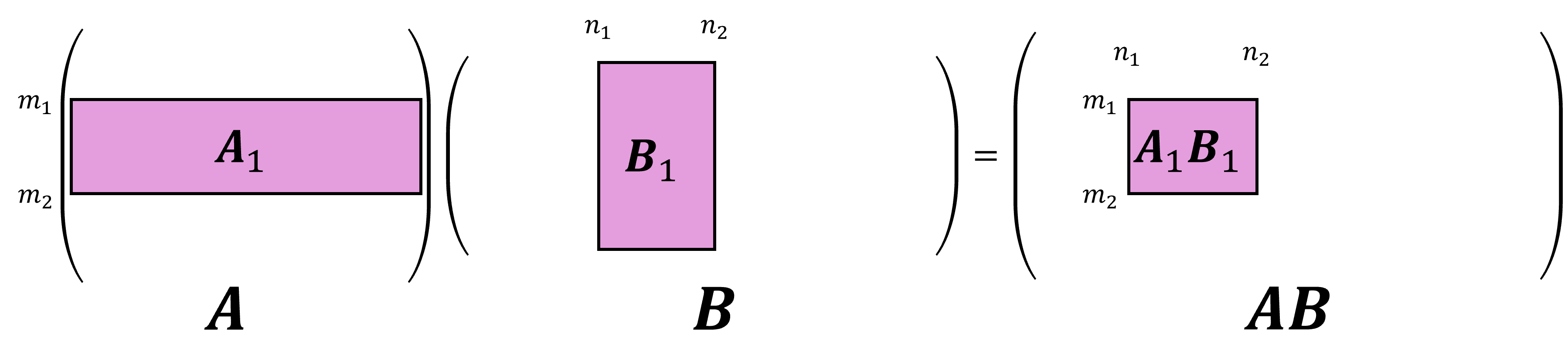
Submatrix
- A submatrix of an matrix , with is formed by taking a block of the entries of the matrix
- Block multiplication:
Special Types of Matrices
- Vectors: a matrix is a (column) vector, and a matrix is a (row) vector. By default, a vector is a column vector
- Zero matrix: All entries are zero, denoted
- Square matrix: It has the same number of rows and columns, a matrix is a square matrix of order
- Diagonal matrix: All entries not along the diagonals are zero, can be denoted as , where is the -entry
- Scalar matrix: A diagonal matrix where all the diagonals are the same constant:
- Identity matrix: A scalar matrix where the constant is 1:
- Upper triangular matrix: square matrix where all values below the diagonal (not including the diagonal) are zero
- Strictly upper triangular matrix: upper triangular matrix, but all values on the diagonal are also zero
- Lower/Strictly lower triangular matrix: same as upper
- Symmetric matrix: the ij entry is equal to the ji entry (the matrix is reflected about the diagonal) ()
Operations
Scalar multiplication & Addition
- Scalar multiplication: Multiply each element in the matrix by the scalar value
- Addition: Add each corresponding element together
- Properties for matrices , and
- Commutative
- Associative
- Additive identity
- Additive inverse
- Distributive
- Scalar addition
- Associative
- if , then either or
Matrix Multiplication
- is pre-multiplied to means
- is post-multiplied to means
- Properties for matrices with sizes for the operations to be well defined
- Not commutative
- Associative:
- Left distributive law:
- Right distributive law:
- Commute with scalar multiplication:
- Multiplicative identity: for matrix ,
- Nonzero zero divisor: There exists and such that
- Zero matrix: and
Power
- Power can only be applied to square matrices, defined as:
- (identity)
- , for
Transpose
- Transpose of matrix , or , is a matrix where the entry of is the entry of
- Write the rows as columns or columns as rows (first row of is first column of )
- Properties
- , or
Elementary Row Operations
- Exchanging two rows:
- Adding a multiple of a row to another
- Multiplying a row by a nonzero constant
- An elementary matrix is a square matrix that corresponds to an elementary row operation. Pre-multiplying a matrix by an elementary matrix is the same as performing the elementary row operation
- Obtained by performing the corresponding row operation to the identity matrix
- Inverse of elementary matrix is reverse row operation
- Two augmented matrices are row equivalent if one can be obtained from the other by elementary row operations
- Two linear systems have the same solution if their augmented matrices are row equivalent
- This means that we can solve a linear system by converting it to REF by performing elementary row operations
Inverse
- Inverse of a square matrix is , then
- Inverse is denoted
- A matrix is invertible if its inverse exists. Otherwise, it is non-invertible
- A non-invertible square matrix is called a singular matrix
- The inverse of a matrix is inverse
- A matrix is invertible iff
- Finding inverse of any matrix:
- If after RREF, the left side is not identity matrix, then the matrix is not invertible
- These statements are equivalent, for square matrix
- is invertible
- is invertible
- has a left-inverse:
- has a right-inverse:
- The RREF of is
- can be expressed as a product of elementary matrices
- Homogeneous system only has trivial solution
- For any , the system is consistent
- Properties (let be order n invertible matrix)
- For nonzero real number , is invertible with inverse
- is invertible with inverse
- if is order n invertible matrix, then is invertible, with inverse
LU Factorisation
- Turn matrix into REF
- Write the elementary matrices corresponding to the operations to get REF (U matrix)
To solve Linear system:
- For the system , let
- , let , so
- Solve , then solve