Logic Gates
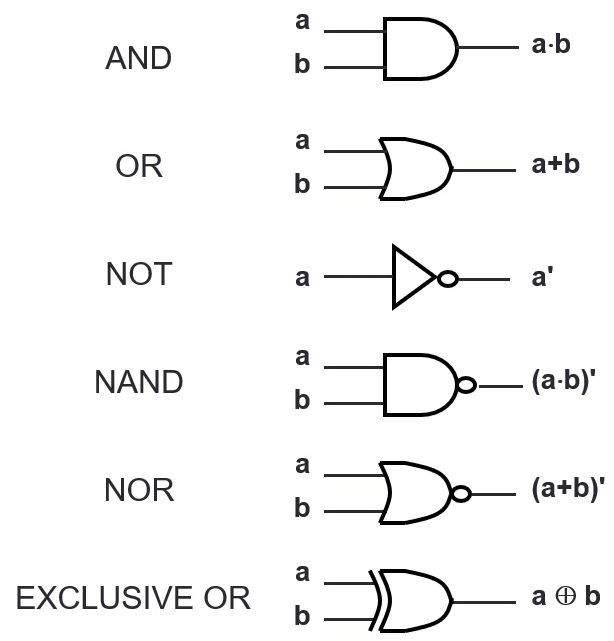
XOR
- A B = (A + B) (A B)’ = A’ B + A B’
- XNOR: (A B)’ or A B
| A | B | A B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Logic Circuits
- Fan-in: the number of inputs of a gate
- Every input must be connected in a working circuit
- Gates may have a fan-in of more than 2
Example: F2 = x + y’ z
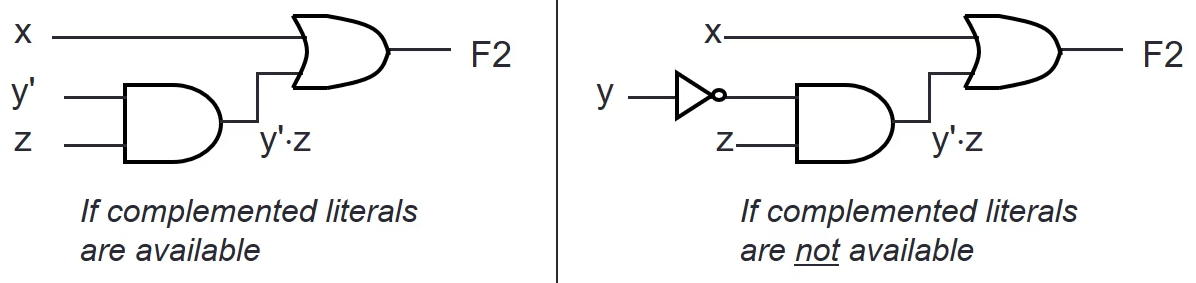
-
AND, OR, NOT gates are sufficient for building any boolean function
- {AND, OR, NOT} is called a complete set of logic
-
However, other gates are also used because:
- They replace many AND, OR & NOT gates (e.g. XOR)
- Economical
- Self-sufficient or universal (e.g. NAND/NOR)
-
Universal gates: a gate that itself is a complete set of logic
- e.g. {NAND} is a complete set of logic (NAND: (A B)’)
- NOT x = (x x)’
- x AND y = ((x y)’ (x y)’)’ (i.e. NOT (X NAND Y) )
- x OR y = ((x x)’ (y y)’)’ (i.e. (NOT X) NAND (NOT Y) )
- e.g. {NOR} is a complete set of logic (NOR: (A + B)’)
- NOT x = (x + x)’
- x AND y = ((x + x)’ + (x + x)’)’
- x OR y = ((x + y)’ + (x + y)’)’
- e.g. {NAND} is a complete set of logic (NAND: (A B)’)
-
A Sum of Products expression can be easily implemented using 2-level AND-OR circuit, or 2-level NAND circuit
- e.g. F = A B + C’ D + E (the 3 diagrams below all represent F)
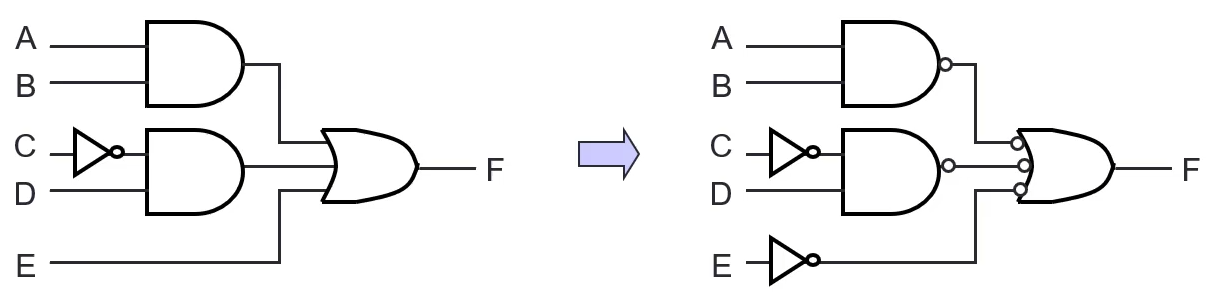
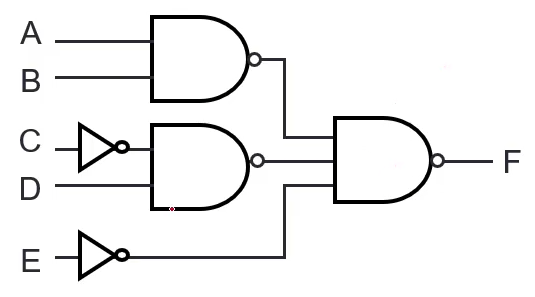
- e.g. F = A B + C’ D + E (the 3 diagrams below all represent F)
-
A Product of Sums expression can be easily implemented using 2-level OR-AND circuit, or 2-level NOR circuit
- e.g. G = (A + B) (C’ + D) E (the 3 diagrams below all represent G)
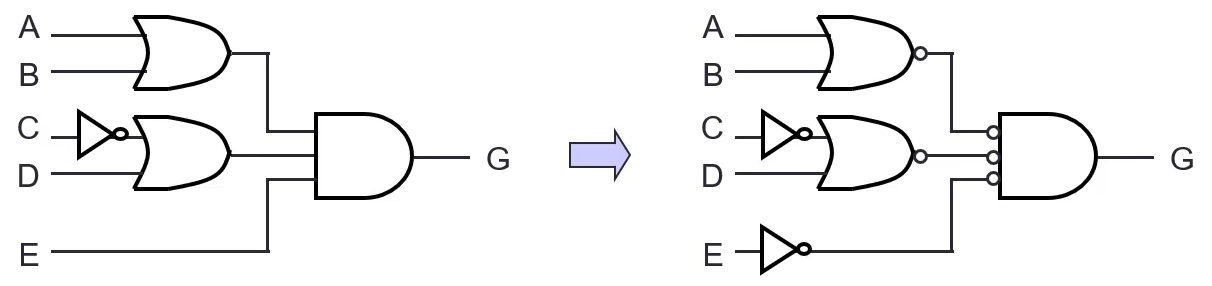
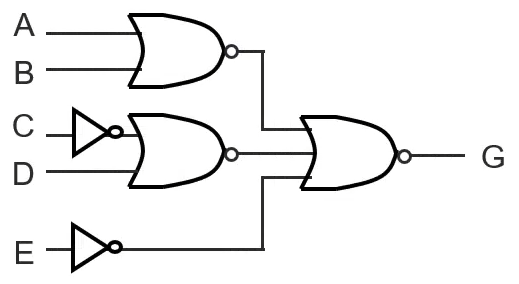
- e.g. G = (A + B) (C’ + D) E (the 3 diagrams below all represent G)
Integrated Circuit (IC)
- A chip that contains a circuit
- Programming Logic Array (PLA): A programmable IC that implements sum-of-products circuits (might allow multiple outputs)
- 2 stages: AND gates (to get all product terms) & OR gates (to get outputs)
- Connection between the stages (or planes) can be “burned” (or programmed)
Half Adder
- inputs: X, Y; outputs: C, S
- In canonical form (sum of minterms)
- C = X Y
- S = X’ Y + X Y’
- S can be simplified to X Y
| X | Y | C | S |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |