What Is it
A pair represents two values (they can be of any data type)
Representing Lists
Pairs can be used to represent lists. This is a list containing 1, 2, 3:
pair(1, pair(2, pair(3, null)))null represents an empty list.
Box Notation
pair(x, y) can be written as [x, y].
so,
pair(1, pair(2, pair(3, null)))can be written as [1, [2, [3, null]]]
For CS1101S
These are the same
list(1, 2, 3)
pair(1, pair(2, pair(3, null)))
[1, [2, [3, null]]]List Notation
Same as box notation, but any sub-structure that is a list is formatted and printed as list(...), so
display_list(pair(pair(7,8), pair(1, pair(2, null))))
list([7, 8], 1, 2) // the pair [7, 8] is the first element in the listBox and Pointer Diagram
draw_data(pair(1, pair(2, pair(3, null))))will display:
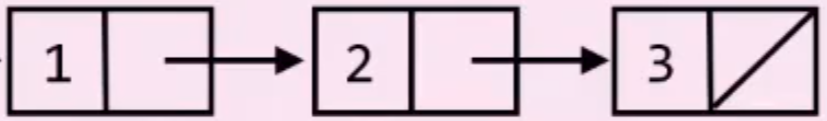
Head and Tail
const x = pair(1, 2)
head(x) // is 1
tail(x) // is 2List Length
List length is counted starting from the tail (null)
The length of a non-empty list is one more than the length of its tail